Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Kimura, Atsushi; Endo, Shunsuke; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(9), p.1133 - 1142, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In recent years, research has been advanced on lead-cooled fast reactors and accelerator drive systems, and it is required to improve the accuracy of the neutron capture cross section of Pb isotopes. Although  Pb has a small natural abundance, it is of importance because it produces the long-lived radionuclide
Pb has a small natural abundance, it is of importance because it produces the long-lived radionuclide  Pb (17.3 million years) by neutron capture reaction. However, it is difficult to measure its cross section by a conventional activation method using a nuclear reactor because the induced radioactivity of
Pb (17.3 million years) by neutron capture reaction. However, it is difficult to measure its cross section by a conventional activation method using a nuclear reactor because the induced radioactivity of  Pb is weak. Hence, the cross-section measurement was performed by applying mass spectrometry. This presentation gives the details of the experiment and the results obtained in the neutron capture cross-section measurement of
Pb is weak. Hence, the cross-section measurement was performed by applying mass spectrometry. This presentation gives the details of the experiment and the results obtained in the neutron capture cross-section measurement of  Pb using mass spectroscopy.
Pb using mass spectroscopy.
Miyahara, Shinya*; Arita, Yuji*; Nakano, Keita; Maekawa, Fujio; Sasa, Toshinobu; Obayashi, Hironari; Takei, Hayanori
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 403, p.112147_1 - 112147_17, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is important to evaluate the inventories and the release and transport behavior of the spallation products (SPs) in the Lead-Bismuth Eutectic (LBE) coolant system of Accelerator Driven System (ADS) for the safety studies of the radiological hazard both in the cases of normal operation and accident. University of Fukui and JAEA have been developing the computer analysis code TRAIL (Transport of RAdionuclides In Liquid metal systems) which predicts the time dependent behavior of SPs within the LBE coolant system of ADS for the wide range of operational events. The source term of both radioactive and stable SPs in the LBE coolant is given as input and the radioactive decay chain model for the radioactive SPs is implemented in the code to evaluate the effect of precursors on the SPs mobility. This paper presents the recent advancement status of the code development and the validation results comparing with the distribution data of volatile SPs in MEGAPIE spallation target.
Katano, Ryota; Oizumi, Akito; Fukushima, Masahiro; Pyeon, C. H.*; Yamamoto, Akio*; Endo, Tomohiro*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 20 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this study, we have demonstrated that data assimilation using lead and bismuth sample reactivities measured in the Kyoto University Critical Assembly A-core can successfully reduce the uncertainty of the coolant void reactivity in accelerator-driven systems derived from inelastic-scattering cross-sections of lead and bismuth. We re-evaluated and highlighted the experimental uncertainties and correlations of the sample reactivities for the data assimilation formula. We used the MCNP6.2 code to evaluate the sample reactivities and their uncertainties, and performed data assimilation using the reactor analysis code system MARBLE. The high-sensitivity coefficients of the sample reactivities to lead and bismuth allowed us to reduce the cross-section-induced uncertainty of the void reactivity of the accelerator-driven system from 6.3% to 4.8%, achieving a provisional target accuracy of 5% in this study. Furthermore, we demonstrated that the uncertainties arising from other dominant factors, such as minor actinides and steel, can be effectively reduced by using integral experimental data sets for the unified cross-section dataset ADJ2017.
Ariyoshi, Gen; Obayashi, Hironari; Sasa, Toshinobu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1071 - 1088, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)Electromagnetic induction method is one of the effective techniques for local velocity measurement in heavy liquid metals. Ricou and Vives' probe and Von Weissenfluh's probe are famous instrumentations using a permanent magnet. However, sensitivity and measurement volume of the probes show unexpected variation since demagnetization of the magnet is occurred by temperature increase up to the Curie temperature. In this study, electromagnetic probe incorporating a miniature electromagnet was newly developed to overcome such unexpected variation. The diameter and the length of the sensor was 6 mm and 155 mm, respectively. The sensitivity and the measurement volume of the probe were assessed by measurement of local velocity of flowing mercury in a square channel. To clarify the validity for the measured velocity profiles, numerical velocity profiles were calculated and compared with experiment. And the validity for the measured velocity profiles were confirmed by calculated result.
Komatsu, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2021-019, 24 Pages, 2022/05
In order to reduce the corrosion rate of materials in molten lead bismuth eutectic (LBE), it is important to adjust the oxygen concentration, and past reports show that the oxygen concentration is often adjusted to about 10 to 10
to 10 wt%. However, it is not clearly stated what concentration is optimal, and there are some reports of severe corrosion even within this concentration range. In this study, a corrosion model considering diffusion in oxide and LBE was developed for 9Cr-1Mo steel, and the corrosion control method estimated from the corrosion model were investigated. We also tried to calculate the optimum oxygen concentration to prevent the flow blockage at the low temperature of loop environment while reducing the corrosion of 9Cr-1Mo steel in molten LBE. As a result, it was expected that the corrosion mode of 9Cr-1Mo steel in LBE could be classified into three types, dense film formation, precipitation film formation, and film dissolution, depending on the ratio of oxide film thickness to diffusion layer thickness, iron concentration in LBE, and temperature. In order to inhibit corrosion, it is important to adjust the oxygen concentration so that the conditions for dense film formation can be maintained. For this purpose, it was expected that a pre-oxidized film of more than 10
wt%. However, it is not clearly stated what concentration is optimal, and there are some reports of severe corrosion even within this concentration range. In this study, a corrosion model considering diffusion in oxide and LBE was developed for 9Cr-1Mo steel, and the corrosion control method estimated from the corrosion model were investigated. We also tried to calculate the optimum oxygen concentration to prevent the flow blockage at the low temperature of loop environment while reducing the corrosion of 9Cr-1Mo steel in molten LBE. As a result, it was expected that the corrosion mode of 9Cr-1Mo steel in LBE could be classified into three types, dense film formation, precipitation film formation, and film dissolution, depending on the ratio of oxide film thickness to diffusion layer thickness, iron concentration in LBE, and temperature. In order to inhibit corrosion, it is important to adjust the oxygen concentration so that the conditions for dense film formation can be maintained. For this purpose, it was expected that a pre-oxidized film of more than 10 m should be applied before immersion in LBE. The oxygen concentration of about 10
m should be applied before immersion in LBE. The oxygen concentration of about 10 to 10
to 10 wt% is the appropriate oxygen concentration when the oxide film has grown to some extent, and a higher oxygen concentration was expected to be required when the film is thin.
wt% is the appropriate oxygen concentration when the oxide film has grown to some extent, and a higher oxygen concentration was expected to be required when the film is thin.
Sasa, Toshinobu
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 98(5), p.211 - 215, 2022/05
Lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) alloy is promising as a spallation target for next-generation reactor coolants and accelerator drive systems (ADS) due to its nuclear and chemical properties. LBE is a heavy metal, and it has good properties both as a spallation target and as a coolant for nuclear transmutation systems of long-lived radioactive nuclei. On the other hand, to improve compatibility with structural materials is one of the major issues in its utilization. The latest research results such as high-temperature operation of LBE and oxygen concentration control to ensure corrosion resistance with the aim of early commercialization of nuclear conversion technology by ADS is introduced.
Obayashi, Hironari; Yamaki, Kenichi*; Yoshimoto, Hidemitsu*; Kita, Satoshi*; Wan, T.*; Sasa, Toshinobu
JAEA-Technology 2021-035, 66 Pages, 2022/03
Construction of Transmutation Experimental Facility (TEF) is under planning in Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) program to promote R&Ds on realization of transmutation technology by an accelerator driven system (ADS). As a facility of TEF, ADS Target Test Facility (TEF-T) will provide a spallation target to study target technology and perform post irradiation examination (PIE) of candidate materials of ADS. In ADS, lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) alloy is used as a spallation target material and a core coolant. As is well known, LBE has corrosive to structural materials hence each component of the target system should provide compatibility with LBE. In addition, instrumentations for LBE are restricted by the target operation condition such as high temperature and irradiation environment. The devices for LBE have been developed individually to achieve the LBE target system. "Integrated Multi-functional MOckup for TEF-T Real-scale TArget Loop, IMMORTAL" was fabricated as a mock-up test loop of the target for the purpose of the integration testing of individually developed devices. This report describes an overview of IMMORTAL and the design of the installed devices.
Nakano, Keita; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nishihara, Kenji; Meigo, Shinichiro; Sugawara, Takanori; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Takeshita, Hayato*; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Research 2021-018, 41 Pages, 2022/03
Neutronic analysis of beam window of the Accelerator-Driven System (ADS) proposed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducted using PHITS and DCHAIN-PHITS codes. We investigate gas production of hydrogen and helium isotopes in the beam window, displacement per atom of beam window material, and heat generation in the beam window. In addition, distributions of produced nuclides, heat density, and activity are derived. It was found that at the maximum 12500 appm H production, 1800 appm He production, and damage of 62.1 DPA occurred in the beam window by the ADS operation. On the other hand, the maximum heat generation in the beam window was 374 W/cm . In the analysis of LBE,
. In the analysis of LBE,  Bi and
Bi and  Po were found to be the dominant nuclides in decay heat and radioactivity. Furthermore, the heat generation in the LBE by the proton beam was maximum around 5 cm downstream of the beam window, which was 945 W/cm
Po were found to be the dominant nuclides in decay heat and radioactivity. Furthermore, the heat generation in the LBE by the proton beam was maximum around 5 cm downstream of the beam window, which was 945 W/cm .
.
Sugawara, Takanori; Watanabe, Nao; Ono, Ayako; Nishihara, Kenji; Ichihara, Kyoko*; Hanzawa, Kohei*
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has investigated an accelerator-driven system (ADS) to transmute minor actinides (MAs) included in high level wastes discharged from nuclear power plants. The ADS is a lead-bismuth cooled tank-type reactor with 800 MW thermal power. It is supposed that the ADS is safer than conventional critical reactors because it is operated in a subcritical state. The previous study performed the transient analyses for the typical ADS accidents such as unprotected loss of flow or beam overpower. It was shown that all calculation cases except loss of heat sink (LOHS) satisfied the no-damage criteria. To avoid the damage by LOHS, the ADS equips Direct Reactor Auxiliary Cooling System (DRACS) to remove the decay heat. The most important points of a DRACS operation are its reliability and to ensure the flowrate in a natural circulation state. This study aims to perform the CFD analysis of the natural circulation to clarify the flowrate in the ADS reactor vessel.
Pyeon, C. H.*; Yamanaka, Masao*; Fukushima, Masahiro
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 195(8), p.877 - 889, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:65.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)Uncertainty quantification of lead (Pb) and bismuth (Bi) sample reactivity worth is numerically determined using the SCALE6.2 code system and experimental results obtained from the solid-moderated and solid-reflected core at the Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA) to demonstrate the sensitivity coefficients of aluminum (Al) and Bi scattering reactions. From the results of the numerical analyses, the impact of  Al and
Al and  Bi scattering cross sections obtained using SCALE6.2/TSAR is disclosed on the Bi sample reactivity worth using Al reference and Bi test samples, although the uncertainty itself is small in the Bi sample reactivity worth.
Bi scattering cross sections obtained using SCALE6.2/TSAR is disclosed on the Bi sample reactivity worth using Al reference and Bi test samples, although the uncertainty itself is small in the Bi sample reactivity worth.
Shamoto, Shinichi; Lee, M. K.*; Fujimura, Yuki; Kondo, Keietsu; Ito, Takashi; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Yasuda, Satoshi; Chang, L.-J.*
Materials Research Express (Internet), 8(7), p.076303_1 - 076303_6, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Pb, Ga, and Ga doped lead free Sn-Ag-Cu solders are used to study the gallium effect for the low joint resistivity with silver sheathed DI BISCCO type H tapes. The results are reported.
Miyajima, Yusuke*; Saito, Ayaka*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Hirata, Takafumi*
Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 45(1), p.189 - 205, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:21.77(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Uncertainty for elemental and isotopic analyses of calcite by LA-ICP-MS is largely controlled by the homogeneity of the reference materials (RMs) used for normalization and validation. In order to produce calcite RMs with homogeneous elemental and isotopic compositions, we incorporated elements including U, Pb, and rare earth elements into calcite through heat- and pressure-induced crystallization from amorphous calcium carbonate that was precipitated from element-doped reagent solution. X-ray absorption spectra showed that U was present as U(VI) in the synthesized calcite, probably with a different local structure from that of aqueous uranyl ions. The uptake rate of U by our calcite was higher in comparison to synthetic calcite of previous studies. Variations of element mass fractions in the calcite were better than 12% 2RSD, mostly within 7%. The  Pb/
Pb/ Pb ratio in the calcite showed
Pb ratio in the calcite showed  1% variations, while the
1% variations, while the  U/
U/ Pb ratio showed 3-24% variations depending on element mass fractions. Using the synthetic calcite as primary RMs, we could date a natural calcite RM, WC-1, with analytical uncertainty as low as
Pb ratio showed 3-24% variations depending on element mass fractions. Using the synthetic calcite as primary RMs, we could date a natural calcite RM, WC-1, with analytical uncertainty as low as  3%. The method presented can be useful to produce calcite with controlled and homogeneous element mass fractions, and is a promising alternative to natural calcite RMs for U-Pb geochronology.
3%. The method presented can be useful to produce calcite with controlled and homogeneous element mass fractions, and is a promising alternative to natural calcite RMs for U-Pb geochronology.
Maekawa, Fujio
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011042_1 - 011042_6, 2021/03
Development of beam window (BW) materials is one of crucial issues in development of accelerator driven nuclear transmutation systems (ADS). The BW is exposed to high energy protons and spallation neutrons, and also to corrosive lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) alloy at high temperature of about 500 C. Recently, not only high-power accelerators but also high-power targets are the rate-limiting factor for increasing the power of accelerator facilities in terms of radiation damage and heat removal. To study radiation damage on BW and target materials for high-power accelerator facilities including ADS, we are planning a materials irradiation facility by utilizing the proton beam of 400 MeV and 250 kW provided by the J-PARC's Linac. The target is flowing LBE alloy which is a candidate target and coolant material of ADS. When a steel sample is irradiated in the target for one year, the sample receives radiation damage of about 10 dpa at maximum which is equivalent to the yearly radiation damage of ADS's BW. In the current facility concept, the facility is equipped with a hot-laboratory for efficient post-irradiation examination. The facility will be outlined in this presentation.
C. Recently, not only high-power accelerators but also high-power targets are the rate-limiting factor for increasing the power of accelerator facilities in terms of radiation damage and heat removal. To study radiation damage on BW and target materials for high-power accelerator facilities including ADS, we are planning a materials irradiation facility by utilizing the proton beam of 400 MeV and 250 kW provided by the J-PARC's Linac. The target is flowing LBE alloy which is a candidate target and coolant material of ADS. When a steel sample is irradiated in the target for one year, the sample receives radiation damage of about 10 dpa at maximum which is equivalent to the yearly radiation damage of ADS's BW. In the current facility concept, the facility is equipped with a hot-laboratory for efficient post-irradiation examination. The facility will be outlined in this presentation.
Sugawara, Takanori; Komatsu, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2020-016, 44 Pages, 2021/01
It is required to control the oxygen concentration in lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) to prevent the corrosion of structures in LBE-cooled nuclear system. This study estimated the oxygen consumption amount in the LBE-cooled accelerator-driven system (ADS). We used the evaluation formula for the oxide layer thickness, which were derived by various experiments, to estimate the oxygen consumption amount. It was found that the maximum oxide layer thicknesses for the fuel assembly and the beam window were about 35 [ m] and 20 [
m] and 20 [ m], respectively. Based on these results, the oxygen consumption amount for the ADS plant was estimated as 30 [kg] during one cycle (one year). Through this study, it was indicated that an oxygen supply device which could supply 3-4 [g/h] oxygen in the normal operation, 150 [g/h] in the peak and about 30 [kg] during one cycle was necessary.
m], respectively. Based on these results, the oxygen consumption amount for the ADS plant was estimated as 30 [kg] during one cycle (one year). Through this study, it was indicated that an oxygen supply device which could supply 3-4 [g/h] oxygen in the normal operation, 150 [g/h] in the peak and about 30 [kg] during one cycle was necessary.
Chikhray, Y.*; Askerbekov, S.*; Kenzhin, Y.*; Gordienko, Y.*; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
Fusion Science and Technology, 76(4), p.494 - 502, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sato, Junya; Shiota, Kenji*; Takaoka, Masaki*
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 385, p.121109_1 - 121109_9, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:43.42(Engineering, Environmental)Lead is a hazardous heavy metal that can be stabilized by incorporation into the matrix of aluminosilicate bearing phases as they solidify. The actual mechanism by which lead is stabilized, however, continues to be unclear because the individual mechanisms of Pb incorporation into crystalline and amorphous aluminosilicate phases have not yet been studied separately. A detailed investigation of the incorporation of Pb into the amorphous phase of aluminosilicate solids was therefore performed. Amorphous aluminosilicate solids were synthesized with 0.7, 1.5, and 3.7 wt% of Pb from aluminosilicate gel produced from chemical reagents. Based on Raman spectroscopy, the Si-O stretching vibration bond shifted to lower wavenumbers with increasing Pb concentration. This shift suggested that covalent bonding between Pb and O in the matrix of the aluminosilicate solids increased. In addition, sequential extraction revealed that most of the Pb (75-90%) in the aluminosilicate solids was in a poorly soluble form (i.e. reducible, oxidizable, and residual fractions). These findings indicate that most of Pb is bonded covalently to the amorphous phase in aluminosilicate solids.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(3), p.276 - 290, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:24.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper presents an approach to uncertainty estimation of spallation particle multiplicity of lead ( Pb), primarily focusing on proton-induced spallation neutron multiplicity (
Pb), primarily focusing on proton-induced spallation neutron multiplicity (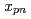 ) and its propagation to a neutron energy spectrum. The
) and its propagation to a neutron energy spectrum. The 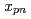 uncertainty is estimated from experimental proton-induced neutron-production double-differential cross sections (DDXs) and model calculations with the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). Uncertainties in multiplicities for
uncertainty is estimated from experimental proton-induced neutron-production double-differential cross sections (DDXs) and model calculations with the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). Uncertainties in multiplicities for 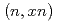 ,
, 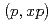 , and
, and 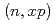 reactions are then inferred from the estimated
reactions are then inferred from the estimated 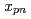 uncertainty and the PHITS calculation. Using these uncertainties, uncertainty in a neutron energy spectrum produced from a thick
uncertainty and the PHITS calculation. Using these uncertainties, uncertainty in a neutron energy spectrum produced from a thick  Pb target bombarded with 500 MeV proton beams, measured in a previous experiment, is quantified by a random sampling technique, and propagation to the neutron energy spectrum is examined. Relatively large uncertainty intervals (UIs) were observed outside the lower limit of the measurement range, which is prominent in the backward directions. Our findings suggest that a reliable assessment of spallation neutron energy spectra requires systematic DDX experiments for detector angles and incident energies below 100 MeV as well as neutron energy spectrum measurements at lower energies below
Pb target bombarded with 500 MeV proton beams, measured in a previous experiment, is quantified by a random sampling technique, and propagation to the neutron energy spectrum is examined. Relatively large uncertainty intervals (UIs) were observed outside the lower limit of the measurement range, which is prominent in the backward directions. Our findings suggest that a reliable assessment of spallation neutron energy spectra requires systematic DDX experiments for detector angles and incident energies below 100 MeV as well as neutron energy spectrum measurements at lower energies below  1.4 MeV with an accuracy below the quantified UIs.
1.4 MeV with an accuracy below the quantified UIs.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Goda, J.*; Oizumi, Akito; Bounds, J.*; Cutler, T.*; Grove, T.*; Hayes, D.*; Hutchinson, J.*; McKenzie, G.*; McSpaden, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 194(2), p.138 - 153, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:61.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)To validate lead (Pb) nuclear cross sections, a series of integral experiments to measure lead void reactivity worth was conducted systematically in three fast spectra with different fuel compositions on the Comet critical assembly of the National Criticality Experiments Research Center. Previous experiments in a high-enriched uranium (HEU)/Pb and a low-enriched uranium (LEU)/Pb systems had been performed in 2016 and 2017, respectively. A follow-on experiment in a plutonium (Pu)/Pb system has been completed. The Pu/Pb system was constructed using lead plates and weapons grade plutonium plates that had been used in the Zero Power Physics Reactor (ZPPR) of Argonne National Laboratory until the 1990s. Furthermore, the HEU/Pb system was re-examined on the Comet critical assembly installed newly with a device that can guarantee the gap reproducibility with a higher accuracy and precision, and then the experimental data was re evaluated. Using the lead void reactivity worth measured in these three cores with different fuel compositions, the latest nuclear data libraries, JENDL 4.0 and ENDF/B VIII.0, were tested with the Monte Carlo calculation code MCNP version 6.1. As a result, the calculations by ENDF/B-VIII.0 were confirmed to agree with lead void reactivity worth measured in all the cores. It was furthermore found that the calculations by JENDL 4.0 overestimate by more than 20% for the Pu/Pb core while being in good agreements for the HEU/Pb and LEU/Pb cores.
Miyahara, Shinya*; Ohdaira, Naoya*; Arita, Yuji*; Maekawa, Fujio; Matsuda, Hiroki; Sasa, Toshinobu; Meigo, Shinichiro
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 352, p.110192_1 - 110192_8, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:48.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Lead-Bismuth Eutectic (LBE) is used as a spallation neutron target and coolant materials of Accelerator Driven System (ADS), and many kinds of elements are produced as spallation products. It is important to evaluate the release and transport behavior of the spallation products in the LBE. The inventories and the physicochemical composition of the spallation products produced in LBE have been investigated for an LBE loop in the ADS Target Test Facility (TEF-T) in J-PARC. The inventories of the spallation products in the LBE were estimated using the PHITS code. The physicochemical composition of the spallation products in the LBE was calculated using the Thermo-Calc code under the conditions of the operation temperatures of LBE from 350 C to 500
C to 500 C and the oxygen concentrations in LBE from 10 ppb to 1 ppm. The calculation showed that the 5 elements of Rb, Tl, Tc, Os, Ir, Pt, Au and Hg were soluble in LBE under the all given conditions and any kinds of compound were not formed in LBE. It was suggested that the oxides of Ce, Sr, Zr and Y were stable as CeO
C and the oxygen concentrations in LBE from 10 ppb to 1 ppm. The calculation showed that the 5 elements of Rb, Tl, Tc, Os, Ir, Pt, Au and Hg were soluble in LBE under the all given conditions and any kinds of compound were not formed in LBE. It was suggested that the oxides of Ce, Sr, Zr and Y were stable as CeO , SrO, ZrO
, SrO, ZrO and Y
and Y O
O in the LBE.
in the LBE.
Ito, Daisuke*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Saito, Yasushi*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya
Journal of Visualization, 22(5), p.889 - 895, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.41(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)